Knowing how our diet affects mental health is essential in our quest for well-being. According to Board-Certified Health and Wellness Coach Dr. Darlene Thomas, our food choices can influence more than just our physical health. Recent studies focus on the connection between nutrition and mental well-being. They share insights about how our diet can both contribute to and alleviate depression.
What Influences Depression
Depression is a complex condition influenced by various factors, including genetic predisposition, negative life events, and health-related issues. In recent studies, nutrition has also emerged as a possible contributor to this condition. The deficiency of essential nutrients, overconsumption of processed foods, and struggles with weight management all disrupt the delicate balance of brain metabolism.
How Our Brain Function Is Affected By Nutrition
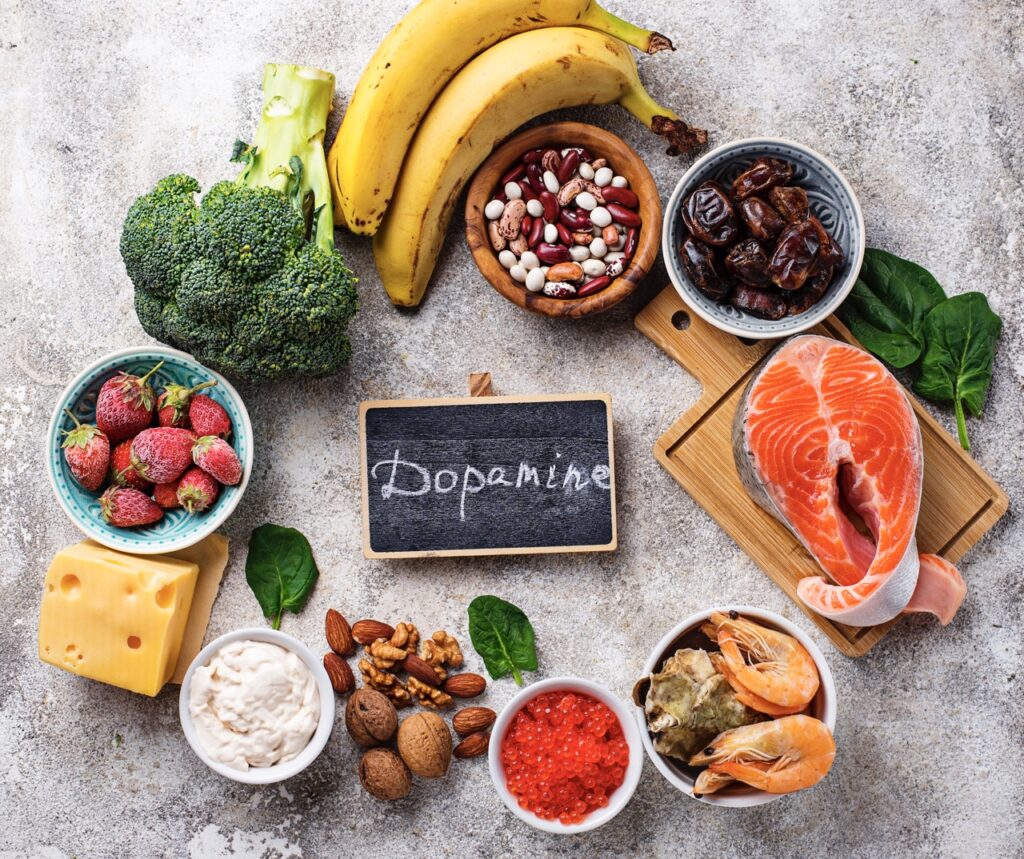
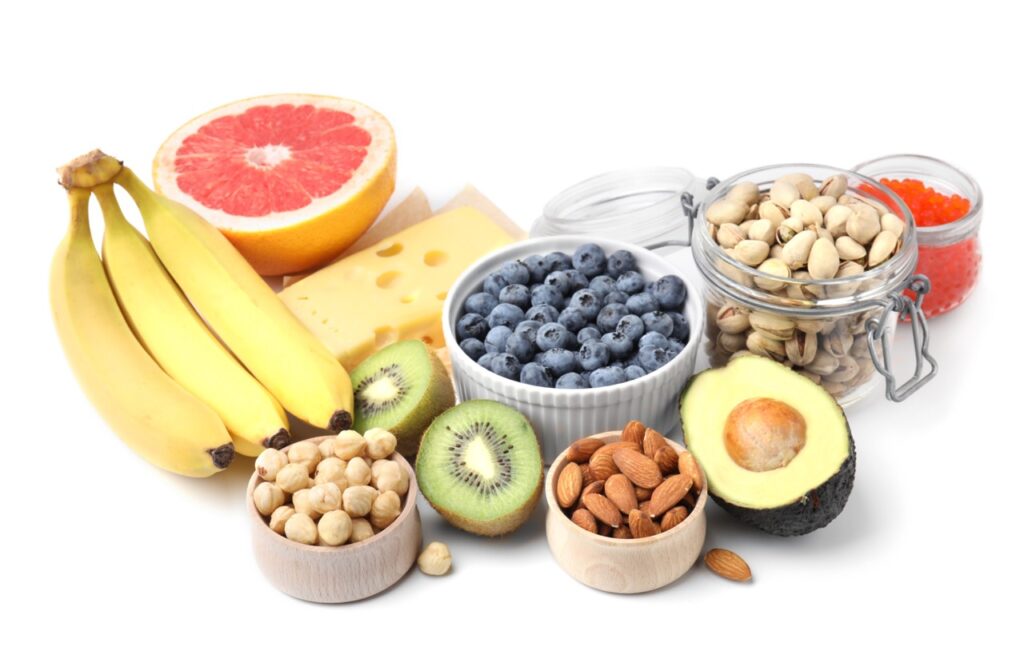


Serotonin Foods
The brain communicates through messengers called neurotransmitters, like serotonin and dopamine. These neurotransmitters facilitate the transmission of crucial information within the brain. They also significantly impact our emotional well-being. Numerous studies reveal the connection between a deficiency in these messengers and the onset of depression.
A delicate balance of amino acids, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals is essential to optimize these neurotransmitters. Unfortunately, people dealing with depression often face challenges in achieving this balance due to a lack of appetite or poor dietary choices.
How Fast Foods And Highly Processed Foods Affect Mental Health
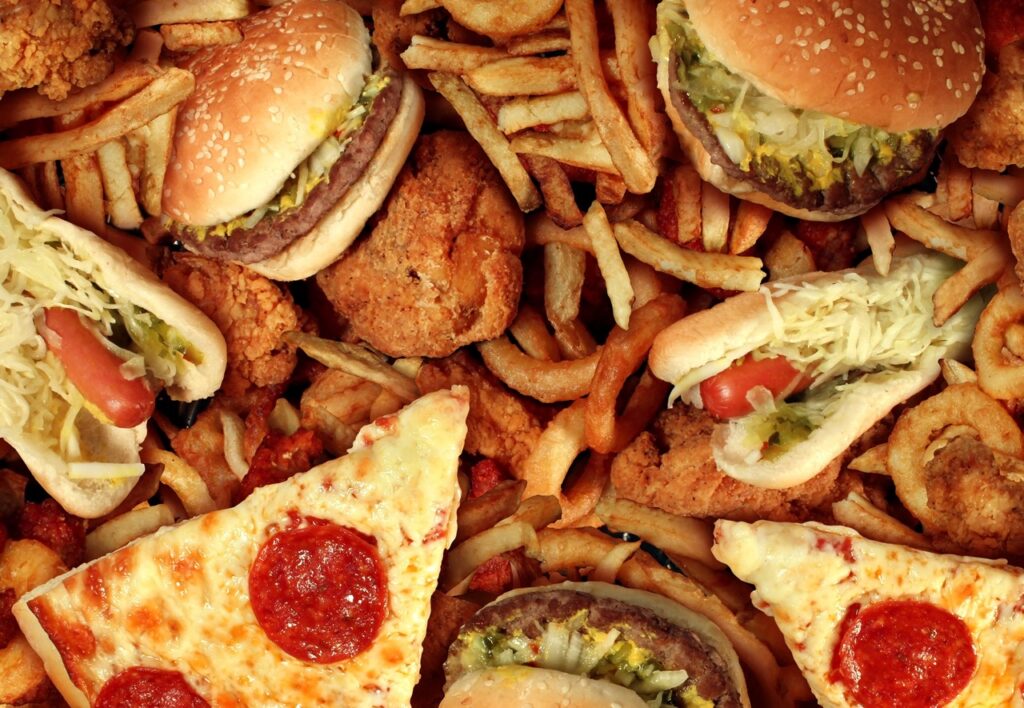

The adverse effects of fast food and highly processed diets on mental well-being is often overlooked. Consuming foods with low nutrient density deprives the body of essential vitamins and minerals. It also hinders the formation of neurotransmitters. Additionally, eating fast foods and highly processed foods can promote micro-inflammation, which further compromises psychological well-being.

The link between nutrition and mental health extends beyond the immediate effects on neurotransmitters. The impact of diet on mental well-being is evident in the connection between obesity and depression. Excessive fat accumulation, especially in the abdominal area, stimulates the production of cytokines, which are proteins that trigger inflammation in the body. This can contribute to the development of depression.
Your Gut and Your Mood
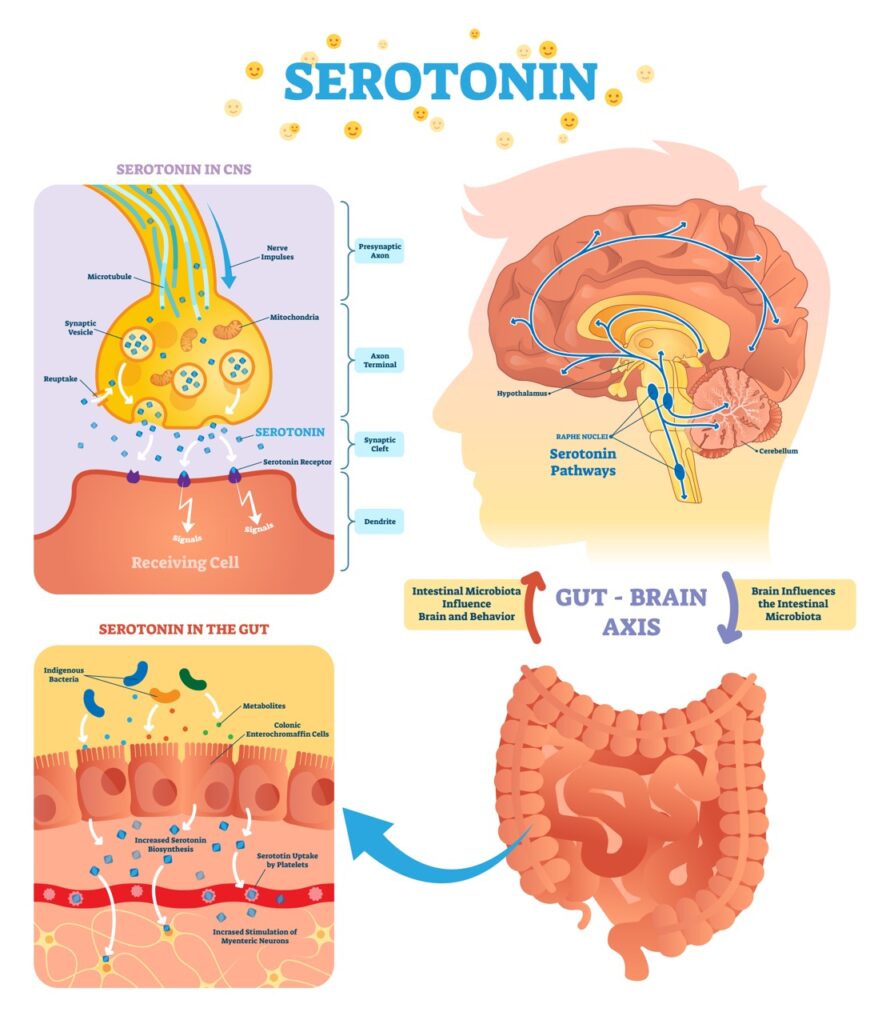
The gut-brain connection offers valuable insights on the impact of nutrition on mental health. Good intestinal bacteria aid in nutrient absorption and produce numerous hormones and neurotransmitters that influence mood and sleep. Maintaining an optimal environment for these beneficial bacteria is crucial for overall well-being.

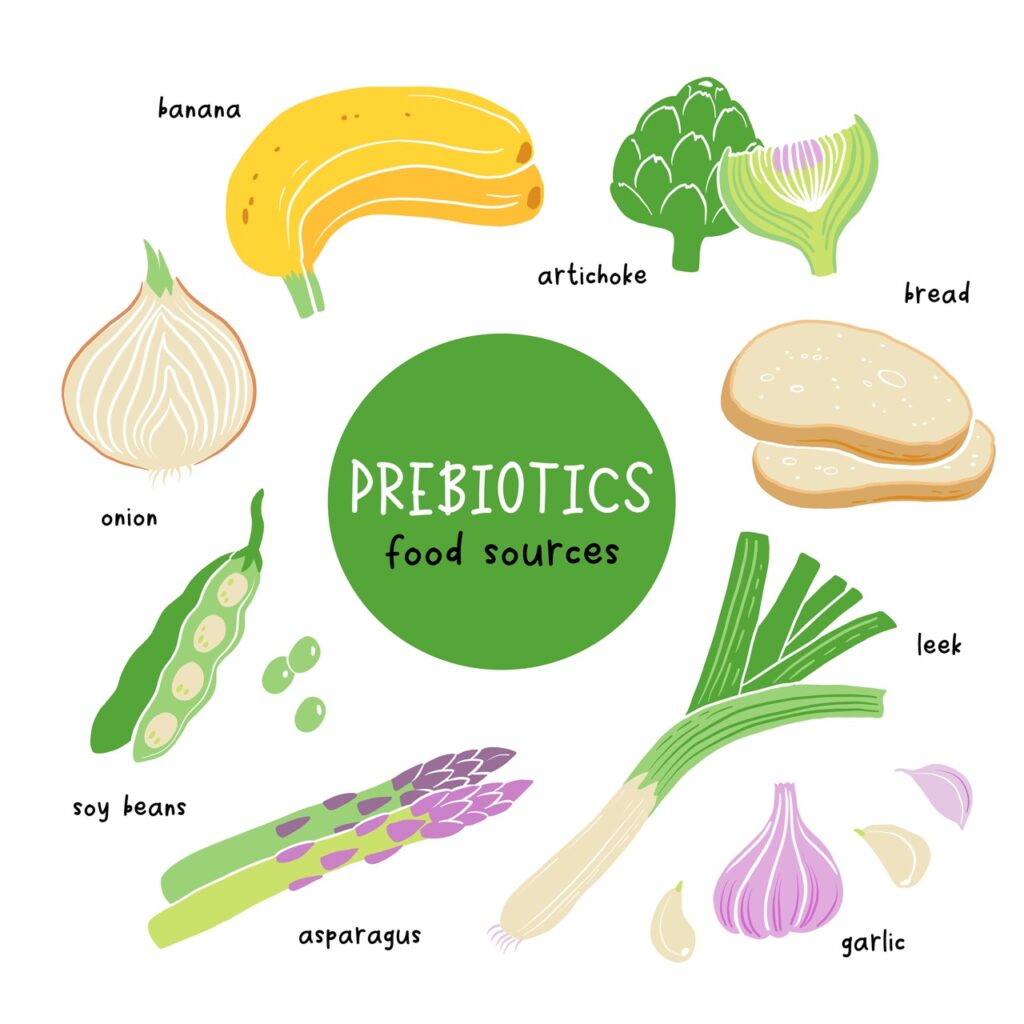
Certain intestinal bacteria, such as probiotics, are essential for a healthy gut. A fiber-rich diet, known as a prebiotic diet, promotes digestion and creates an environment where good intestinal bacteria can thrive. Incorporating mood-boosting foods like psyllium husks, flaxseeds, or chia seeds can help maintain this balance.
How An Anti-Inflammatory Diet Positively Affects Our Mental Health
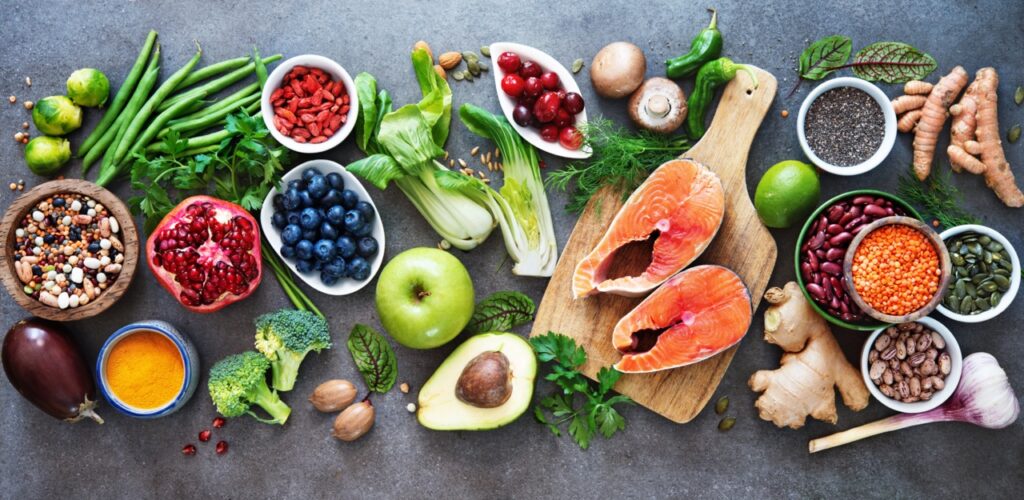

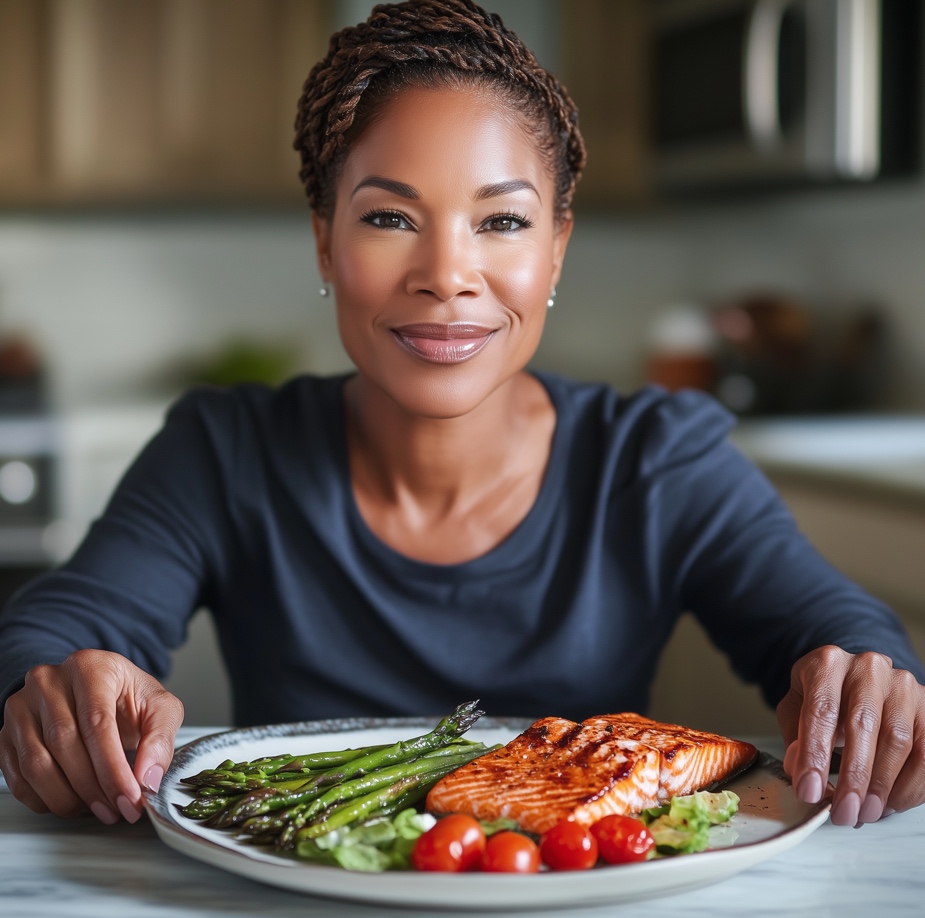
The significance of nutrition in mental health is further emphasized by large-scale studies that recommend an anti-inflammatory eating plan. This includes a variety of low-glycemic fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and nuts (such as walnuts and almonds). Fish, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, is also highlighted for its positive impact on mental wellness.
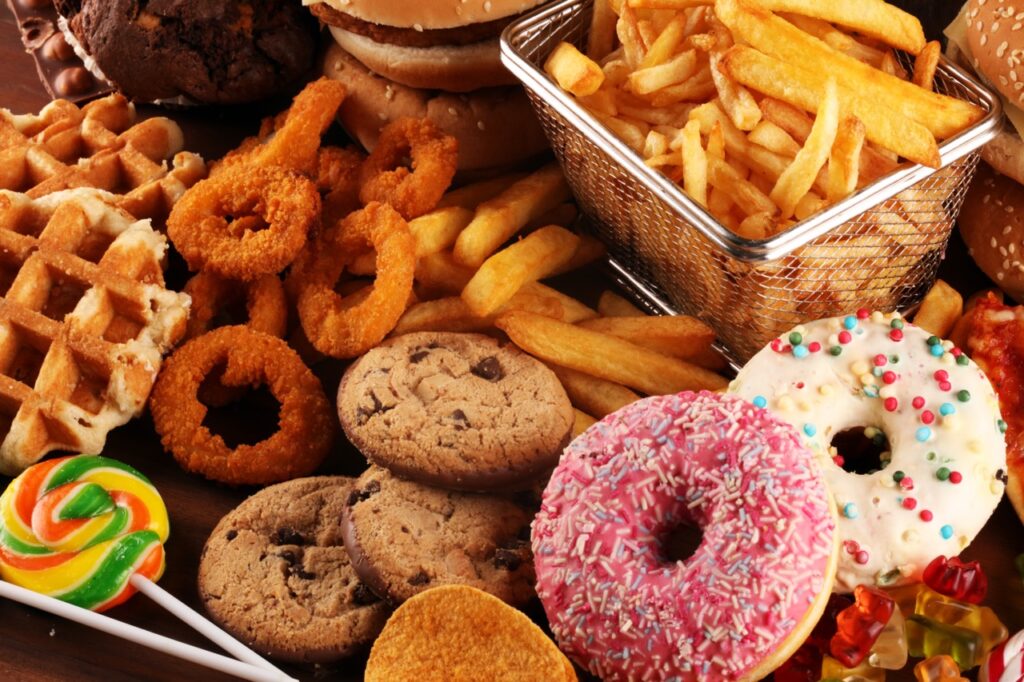

Consumption of pro-inflammatory foods such as sugar, processed foods, and wheat flour should be limited or avoided. This dietary adjustment helps reduce micro-inflammation and cell damage in the body, allowing neurotransmitters to be produced in sufficient quantities. Additionally, it positively affects intestinal bacteria, reinforcing the link between gut health and mental well-being.

By understanding and making informed dietary choices, you can empower yourself to combat depression and improve your overall well-being. Contact Dr. Darlene if you need assistance in this journey toward improved mental health and well-being.








